Cataract Surgery – Preparation and Precautions
Cataracts refer to the clouding of the eye lens, affecting one’s ability to read, drive, and recognize facial expressions. Most cataracts develop gradually and do not require immediate surgery. However, for those whose vision becomes extremely blurry, cataract surgery may be recommended to remove the eye lens and replace it with an artificial one. The procedure helps one see better. Here are key things to know about the procedure and the condition:
What is cataract surgery?
The eye lens concentrates light so the brain and eye can convert the data into an image. Cataracts results in hazy vision and symptoms like glare and halo effects around bright lights. Cataract surgery is a procedure that removes cloudiness or haze from the eyes. It involves removing the clouded lens and inserting a clear artificial lens to restore vision. Cataracts can develop due to issues like retinopathy, a condition that affects people with diabetes, or age-related changes to the retina.
Diagnosis
As the first step, cataracts are diagnosed using a variety of tests, after which the doctor may determine if surgery is required. After reviewing the patient’s medical history and current symptoms, a healthcare professional may recommend the following tests:
Visual acuity test: This test assesses a person’s ability to read a series of letters using an eye chart. Each eye is examined separately, while the other is covered. The eye doctor determines whether the patient’s vision is impaired using a chart or a viewing device with increasingly smaller letters.
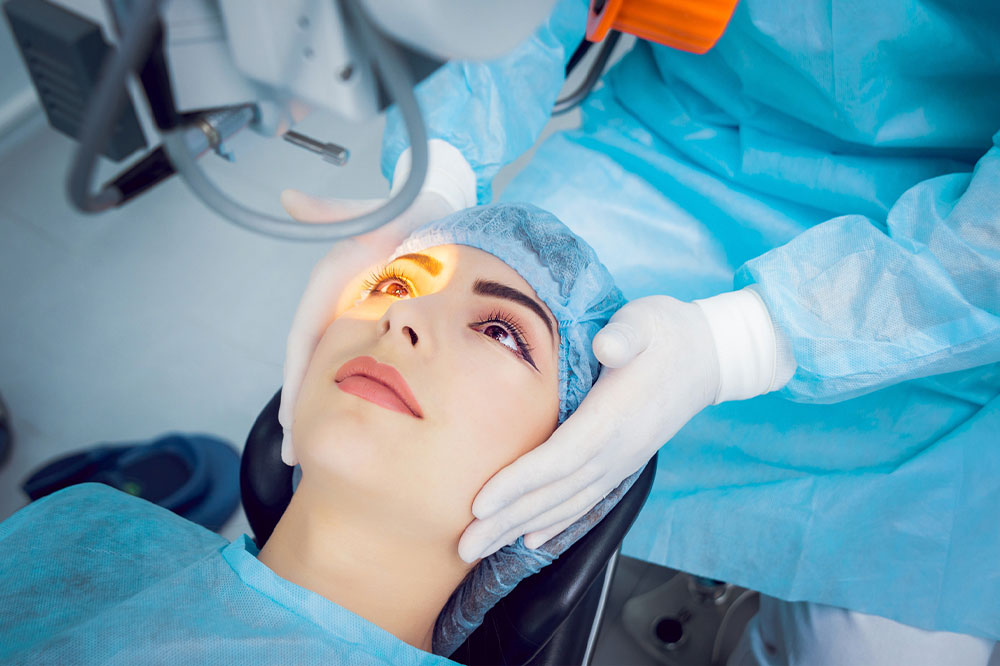
Slit-lamp examinations: Here, a microscope called a slit lamp magnifies the structures in front of the eye, allowing the eye doctor to examine patients. The microscope uses an intense line of light called a slit to illuminate the cornea, iris, lens, and area between the iris and cornea. The instrument allows the physician to view these structures in segments, making it easier to detect any minor anomalies.
Retinal exam: During this test, drops are used to dilate or widen the pupils of the eyes. This makes it easy to examine the back of the eyes (retina). The eye doctor can check for signs of cataracts by inspecting the lens using a slit lamp or a unique tool called an ophthalmoscope.
Applanation tonometry: This test measures the fluid pressure in the eye. Multiple devices can be used to examine the eye here.
Preparing for surgery
Check for changes in eye health: One should keep an eye out for minor changes in vision two weeks before undergoing cataract surgery. They should also avoid contracting an eye infection for a clean and safe operation. If there is any redness, sensitivity, or discharge, one should notify the doctor. It is also important to undergo additional testing scheduled by the doctor before surgery. Notify the healthcare personnel if one observes new symptoms, such as a severe cold or difficulty breathing.
Discuss existing treatment with the doctor: Some prescription treatments can increase the risk of bleeding during the procedure or interfere with cataract surgery. So, one should discuss ongoing treatment for existing conditions with a health professional and see if it should be discontinued for a while. One should stop certain treatments only if a doctor recommends them.
Use eye drops: Eye drops may be administered a few days before the surgery. One should use it as directed at the appropriate time to avoid infection and other complications. The drops can also be used on the day of the surgery, so one should carry them to the clinic or treatment center. One should avoid wearing contact lenses for three days before the cataract surgery, as they could irritate the eyes, resulting in the doctor rescheduling the procedure. One should get plenty of rest and, if necessary, wear glasses.
Plan for aftercare: Most patients return home after treatment, so one should plan ahead and make transportation arrangements. The entire process, from check-in to check-out, takes about three hours. Carrying a pair of non-prescription dark sunglasses to wear after surgery is a crucial measure, as the eyes may have trouble adjusting in the initial hours following the procedure. After the surgery, the doctor might advise limiting activities like bending or lifting, so making arrangements for assistance around the house is essential.
Post-procedure precautions
Avoid driving for a few days: Driving is not recommended after surgery, at least for 3–4 days. Based on the state of the eyes at the first follow-up appointment, the healthcare professional will suggest a time frame after which one can resume regular activities. Prior to this, all precautions must be considered to prevent any danger.
Shield the eyes: After the procedure, a clear shield is put over the eyes to shield them from rubbing, dust, and environmental irritants. One should keep the shield after getting home as it must be worn at night for the next 4 to 5 days after surgery. The lens requires some time to adjust to the light, so one should rest and get used to the differences before removing the shield.
Avoid harsh lighting: One should stay away from bright, flashing lights for at least 24 hours after undergoing cataract surgery. This includes light from the television, mobile phone, tablet, laptop, and other screens. It is important to let the eyes rest, as for a quick recovery, they must heal without being overwhelmed by stimuli.
Other precautions: One should wear dark, UV-blocking sunglasses whenever they step outside in the first few weeks after surgery. For three to four weeks, one should avoid heavy lifting and strenuous exercise. Patients should finish the entire course of antibiotics to prevent infection. One should also ensure that their surroundings are dust-free to avoid experiencing itchy eyes in the first few weeks after the surgery.
Cost of cataract surgery
If the procedure is considered medically essential, one’s insurance provider may pay for the costs. Cataract surgery costs can vary depending on the facility and the type of operation. The procedure could cost around $2,500 in out-of-pocket expenses, including the surgeon’s fee, hospital fees, postoperative care, and anesthesiologist fees. For a more precise figure, one should speak with a professional or a local ophthalmologist.






